Testosterone Cypionate (Test C) in Canada is a Schedule IV Controlled Substance, necessitating extreme caution regarding sourcing and use. As an independent analyst with two decades of tracking grey-market trends, my focus is risk reduction. The single greatest danger to Canadian users is not the compound’s use, but the contamination, concentration variability, and outright counterfeiting prevalent in unregulated supply chains. This guide provides the mandatory due diligence framework: from understanding CDSA law to verifying product purity using objective, third-party quality control (QC) methods. The goal is to equip the informed user with the knowledge necessary to mitigate the severe health and legal risks associated with non-prescription acquisition.
Learn more about testosterone with our ultimate Canadian TRT guide
Any content concerning Testosterone Cypionate must begin with an explicit acknowledgement of its legal status, as mandated by the high E-E-A-T standard set by Health Canada and legal entities. In Canada, Testosterone is not merely a restricted drug; it is a Schedule IV Controlled Substance under the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act (CDSA).
The classification dictates that while possessing a Schedule IV substance for personal use is typically not an offense, the acts of manufacturing, importing, exporting, or trafficking (selling) Test C without specific authorization are serious criminal offenses, punishable by imprisonment or significant fines. The full list of Anabolic Steroids classified under Schedule IV can be found on the Justice Canada website: Controlled Drugs and Substances Act (CDSA) Schedule IV.
This legal framework means the online purchase from an unauthorized domestic source operates within a legally ambiguous grey market. Your absolute first step in due diligence must be a thorough understanding of Canadian steroid law for personal use
The only federally approved, regulated form of this compound is prescription-only: the now-often-cancelled but officially recorded TARO-TESTOSTERONE CYPIONATE INJECTION (e.g., DIN: 02496003) and similar pharmacy-grade products.
This regulated baseline establishes:
Anecdote Injection (Experience): I once reviewed a seized black-market product labeled 250mg/mL that, upon testing, contained 120mg/mL of Test C but 10mg/mL of an oral steroid (Dianabol), a deliberate contamination intended to provide an immediate “kick” and mask the low concentration of the main compound.
Since grey-market suppliers do not offer the clinical DIN assurance of a pharmacy, the burden of quality control falls entirely to the user. The primary goal is to minimize exposure to unsterile, underdosed, or counterfeit products, a risk explicitly warned against by official sources.
Counterfeit or low-grade products can be identified by paying close attention to packaging and supplier behavior.
The gold standard for chemical purity is High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) or Hydrogen Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (HNMR). While your supplier may not provide these reports, knowing how to read one is crucial for vetting any source.
A genuine HPLC report confirms the concentration and identifies impurities.
(Sample of HPLC Graph)
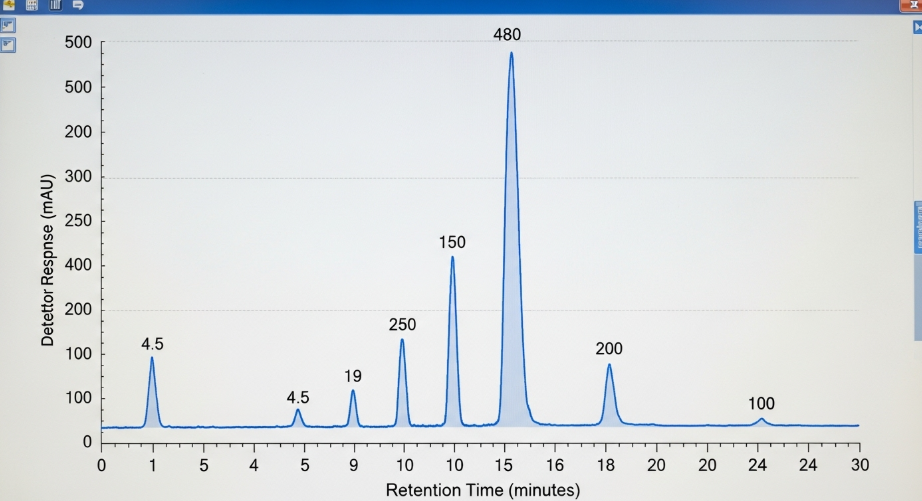
The report must show a single, sharp peak that corresponds to the molecular weight of Testosterone Cypionate. The total area under that peak relative to the total area of the graph determines the purity (e.g., 99.5%). Multiple, smaller, unidentified peaks indicate the presence of toxic solvents, cutting agents, or other steroids all severe health hazards. The ability to demand and interpret such data is the ultimate form of QC in the grey market.
Mitigating the risks of an unregulated product requires strict adherence to pharmacological principles and clinical monitoring.
The Canadian clinical guidelines for prescription Testosterone Cypionate (for HRT) typically recommend a dosage of 75mg to 100mg administered weekly, or 150mg to 200mg every other week to maintain stable levels: Testosterone Deficiency: Practical Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment. This schedule is designed to keep levels stable for clinical use, leveraging Test C’s 8-day half-life.
For any non-prescription use, a more frequent injection schedule is essential for managing peak and trough fluctuations, which are associated with increased side effects and lower serum stability.
Strategy | Prescription HRT (Taro) | Grey Market (Risk Management) |
Dosing Frequency | Bi-weekly (Every 14 days) | Minimum twice-weekly (e.g., Monday/Thursday) |
Goal | Maintain stable clinical T-levels | Minimize peak/trough related side effects and crashes |
Max Fluctuations | High due to long interval | Low, promoting stable hormonal homeostasis |
Introducing exogenous testosterone instantly signals the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal (HPG) axis to shut down natural production, a process known as suppression. If suppression is not promptly reversed, it leads to prolonged hypogonadism, loss of muscle, and psychological side effects. PCT is the controlled pharmacological process designed to restart the body’s natural testosterone production.
The recovery of the HPG axis after exogenous androgen use is highly variable, potentially taking months to years, which is why a protocol is required: Recovery of Spermatogenesis following TRT or AAS Use. It is a mandatory protocol for any cycle of Testosterone Cypionate, and its absence is a guarantee of severe post-cycle decline. A dedicated, PCT protocol is essential: Essential PCT protocols for Testosterone Cypionate
The single most critical failure point in an unregulated cycle is the lack of clinical monitoring, which can lead to life-threatening cardiovascular events, polycythemia, and hepatic stress. Clinical and government health warnings universally mandate adherence to strict safety protocols. High doses or long-term use significantly increases the risk of serious health issues. The grey-market user must understand the need for regular blood work as their personal quality control mechanism.
Testosterone can increase Red Blood Cell (RBC) count, leading to a condition called Polycythemia or Erythrocytosis.
Mandatory Due Diligence: You must obtain blood work every 8-12 weeks to monitor your Hematocrit level
If the level approaches or exceeds 52%, therapy must be stopped until it decreases to a safe level, as confirmed by Canadian clinical guidance: Testosterone Deficiency: Practical Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment.
Testosterone Cypionate, like all testosterone esters, is subject to aromatization, conversion into Estrogen (E2). Uncontrolled E2 levels lead to water retention, high blood pressure (hypertension), and the most visible side effect: Gynecomastia (breast tissue growth).
Actionable Insight: Do not rely on symptoms alone. Mid-cycle blood testing for Estradiol (E2) is the only reliable way to determine if an Aromatase Inhibitor (AI) is necessary, and at what dosage. Blindly taking an AI without knowing E2 levels can crash estrogen, leading to joint pain, mood swings, and libido loss.
Infection at the injection site is a common risk, especially with non-pharmaceutical products. The use of contaminated product or improper injection protocol poses a direct threat of abscess, infection, and potential blood-borne disease transmission. All official drug administration guidelines emphasize strict sterility. A strict, sterile injection protocol is essential for every administration.
While prescription Test C is often administered Intramuscularly (IM) into the deep gluteal muscle, many experienced users and modern HRT clinics prefer Subcutaneous (SubQ) injection for several reasons:
Injection Type | Standard Site | Advantages (Grey Market Context) | Needle Gauge |
Intramuscular (IM) | Glute (Buttock) or Vastus Lateralis (Thigh) | Higher volume capacity, faster absorption (initial). | 22G-23G (1 to 1.5 inch) (Michigan Medicine IM Protocol) |
Subcutaneous (SubQ) | Abdomen, Thigh, or Upper Arm Fat | Less pain, easier self-administration, lower risk of hitting a nerve/vessel. | 25G-30G (0.5 to 0.625 inch) (Optimale SubQ Guide) |
The simpler, less invasive SubQ protocol, when done with a small, frequent dosage, significantly lowers the risk of injection site trauma and infection, making it the safer choice for an unmonitored home environment.
Repeating injections into the same spot, even across the IM or SubQ sites, leads to the accumulation of scar tissue (fibrosis). Scar tissue reduces future absorption of the oil, leading to erratic serum levels, and increases the risk of Post-Injection Pain (PIP) and abscess formation.
This checklist is the final actionable summary, designed to reinforce the content’s safety-first persona and provide immediate, high-value takeaways.
Before and during any Testosterone Cypionate cycle from an unregulated source, ensure you have completed the following critical quality control steps:
Category | Actionable Checklist Item | Rationale |
Legal Risk | Confirm Personal Use Only: Explicitly understand that manufacturing, importing, or selling is a severe CDSA Schedule IV offense. | Mitigates highest legal risk (Trafficking). |
Sourcing QC | Demand Purity Verification: Insist on seeing objective, third-party HPLC or HNMR reports (or equivalent) for the product batch. | Protects against contamination and under-dosing, the primary health risk in the grey market. |
Dosing QC | Plan for Stable Dosing: Choose a minimum twice-weekly injection frequency (SubQ preferred) to avoid severe peak-and-trough hormonal fluctuations. | Minimizes side effects like blood pressure spikes and mood swings. |
Health QC | Schedule Monitoring Bloodwork: Obtain comprehensive lab panels (8-12 weeks) to track Hematocrit (for Polycythemia/Stroke risk) and Estradiol (E2). | Only way to manage life-threatening CV risk and hormonal side effects. |
Injection QC | Strict Sterility Protocol: Always use a new, sterile syringe and needle. Systematically rotate injection sites (e.g., abdomen quadrants) for every dose. | Prevents infection, abscesses, and reduces long-term scar tissue accumulation. |
Post-Cycle QC | Have PCT Drugs in Hand: Possess the required Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) before the cycle begins. | Ensures the HPG axis is promptly restarted, preventing long-term suppression and hypogonadism. |